The integration of e2x is equal to e2x/2. In this post, we will learn how to integrate e to the 2x. The integration of e2x can be derived directly from the formula of the integral of emx which is given below:
∫emx dx = $\dfrac{e^{mx}}{m}$ +C where C is an integration constant.
Putting m=2 in the above formula, the integral of e to the 2x is equal to
∫e2x dx = $\dfrac{e^{2x}}{2}$ +C.
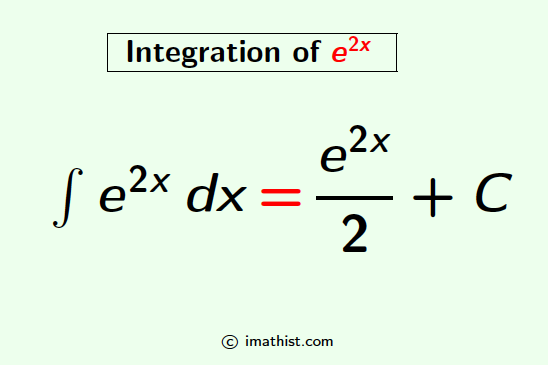
What is the Integration of e2x
Question: What is the integration of e2x?
Answer: The integration of e2x is $\dfrac{e^{2x}}{2}$+C.
Explanation:
We will find the integration of e2x by the substitution method, we will follow the below steps.
Step 1: Let us put $t=2x$.
Differentiating both sides with respect to x, we have
$\dfrac{dt}{dx}=2$
⇒ $dx= \dfrac{dt}{2}$
Step 2: Let us now put the values of 2x and dx in the original integration. By doing so, we will get that
∴ ∫e2x dx = ∫ $e^t \dfrac{dt}{2}$
= $\dfrac{1}{2}$ ∫ et dt as 1/2 is a constant, so we can take it out of the integration.
= $\dfrac{1}{2}$ et +C as the integration of ex is ex
= $\dfrac{1}{2}$ e2x + C as t=2x.
So the integration of e2xdx is $\dfrac{1}{2}$ e2x +C where C is an integral constant.
Verification: To verify the integration of e2x is e2x/2 +C, we need to show that the derivative of e2x/2 +C is equal to e2x.
Now, d/dx (e2x/2 +C)
= d/dx(e2x/2) + d/dx(C)
= 2e2x/2 + 0 as the derivative of a constant is zero and d/dx (eax) = aeax.
= e2x.
So the integration of e2x is equal to e2x/2 +C is verified.
More Integrals: Integral of e3x
Integration of tan x | Integration of cot x
Integration of secx | Integration of cosecx
Definite Integral of e2x
Question: Find the definite integral $\int_0^1 e^{2x} dx$.
Answer:
We have shown above that the integration of $e^{2x} dx$ is $\dfrac{1}{2} e^{2x}$. Thus, we have that
$\int_0^1 e^{2x} dx$
$=[\dfrac{1}{2} e^{2x}]_0^1$
$=\dfrac{1}{2}[e^{2x}]_0^1$
$=\dfrac{1}{2}(e^{2 \cdot 1} -e^0)$
$=\dfrac{1}{2}(e^2 -1)$
So the definite integration of e2x from 0 to 1 is equal to (e2-1)/2.
Also Read:
Derivative of $\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}$
FAQs
Q1: What is the integration of e2x?
Answer: The integration of e2x is e2x/2 +C where C is an integral constant.