The limit of (x^n-a^n)/(x-a) as x approaches a is equal to nan-1. This limit is denoted by limx→a (xn-an)/(x-a), so the limit formula of (xn-an)/(x-a) when x tends to a is given as follows.
| limx→a (xn-an)/(x-a) = n⋅an-1 |
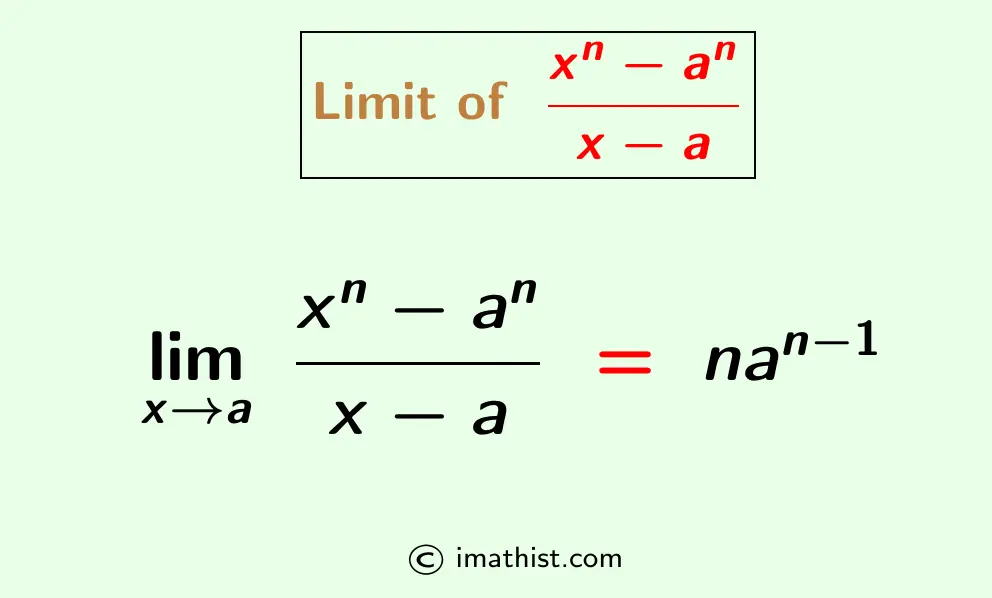
Lets prove this limit formula.
Proof of limx→a (xn-an)/(x-a)
To prove limx→a (xn-an)/(x-a) = n⋅an-1 we will consider three different cases depending upon n is a positive integer, negative integer, or a rational number.
Case 1:
n is a positive integer.
Using the binomial identity: xn-an = (x-a) (xn-1 +xn-2a +…+an-1) we get that
limx→a (xn-an)/(x-a)
= limx→a (xn-1 +xn-2a +…+an-1)
= an-1 +an-2a +…+an-1
= an-1 +an-1 +…+an-1 {n times}
= nan-1.
So the limit of (xn-an)/(x-a) is equal to nan-1 when x tends to a.
Case 2:
n is a negative integer.
Assume n= -m where m is a positive integer.
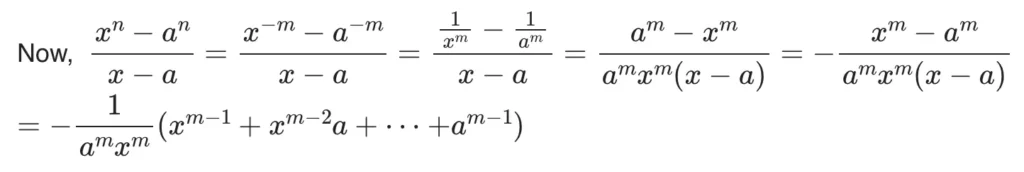
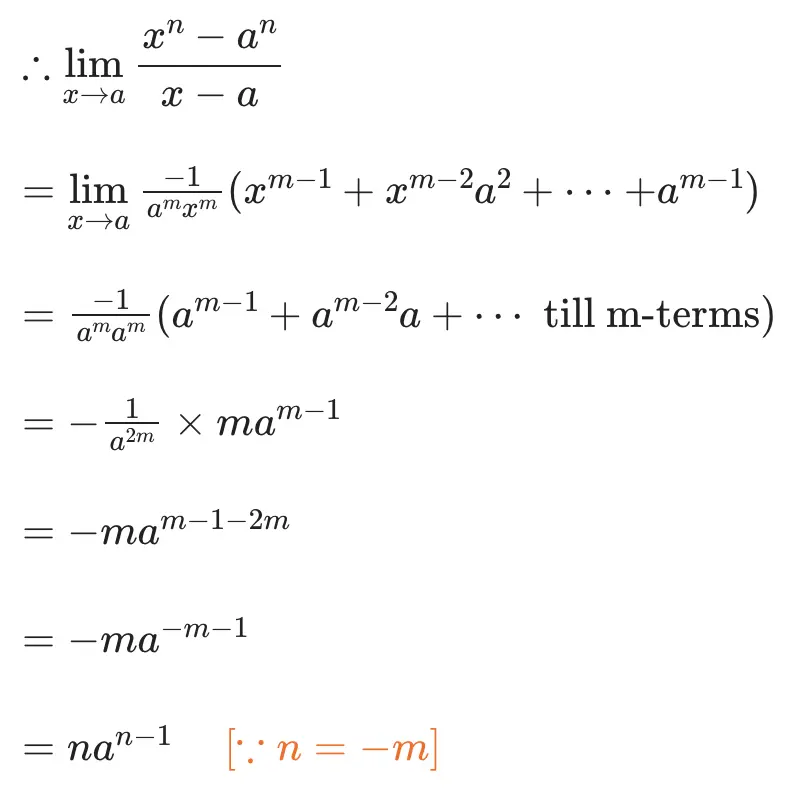
So the limit formula limx→a (xn-an)/(x-a) = nan-1 is valid when n is a negative integer.
Case 3:
n is any real number.
Assume n= p/q where q≠1 is a positive integer and p is either a positive or a negative integer.
Let x1/q = z and a1/q =b.
Therefore, x=zq and a=bq.
Observe, z→b when x→a.
Now,
$\dfrac{x^n-a^n}{x-a}$ $=\dfrac{x^{p/q}-a^{p/q}}{x-a}$ $=\dfrac{z^p-b^p}{z^q-b^q}$ $=\dfrac{\frac{z^p-b^p}{z-b}} {\frac{z^q-b^q}{z-b} }$
Therefore,
limx→a (xn-an)/(x-a)
= limz→b [(zp-bp)/(z-b) / (zq-bq)/(z-b)]
= limz→b (zp-bp)/(z-b) / limz→b (zq-bq)/(z-b)
= pbp-1 /qbq-1
= $\dfrac{p}{q}b^{p-q}$
= $\dfrac{p}{q}a^{\frac{p-q}{q}}$ since a1/q =b.
= $\dfrac{p}{q}a^{\frac{p}{q}-1}$
= nan-1
So the limit of (xn-an)/(x-a) is equal to nan-1 as x approaches a, and this is proved for any real number n. This completes the proof.
More Limits:
Limit of (xn-1)/(x-1) when x→1
FAQs
Q1: What is the limit of (xn-an)/(x-a) when x tends to a?
Answer: The limit of (xn-an)/(x-a) is equal to nan-1 when x tends to a, that is, limx→a (xn-an)/(x-a) = nan-1.