The Laplace transform of sin t is equal to 1/(s2+1), and it is denoted by L{sint}. Here we will find the Laplace of sint by the definition of Laplace transforms.
The formula of the Laplace of sint is given by
L{sint} = $\dfrac{1}{s^2+1}$.
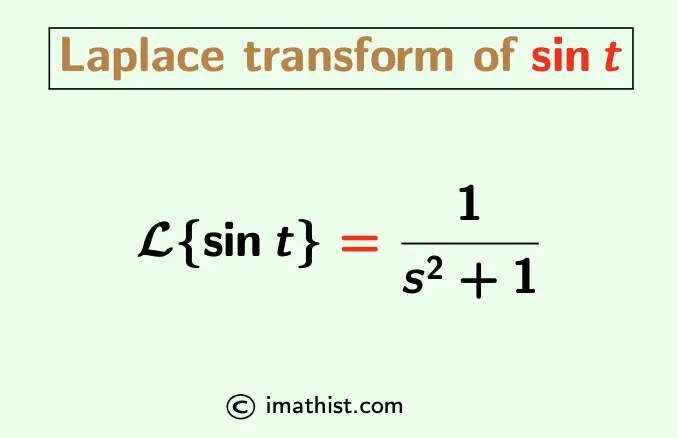
Laplace transform of sint
By definition, the Laplace transform of f(t) is given by
L{f(t)} = $\int_0^\infty$ e-st f(t) dt
Let f(t) = sint.
Then the Laplace of sin t is equal to
L{sin t} = $\int_0^\infty$ e-st sin t dt
= $\Big[\dfrac{e^{-st}}{s^2+1}(-s \sin t – \cos t) \Big]_0^\infty$, using the integration formulas listed here.
= limb→∞ $\Big[\dfrac{e^{-sb}}{s^2+1}(-s \sin b – \cos b) \Big]$ $+ \dfrac {e^{0} (s \sin 0 + \cos 0) } {s^2 + 1}$
= $0+ \dfrac{1}{s^2 + 1}$ as we know sin0=0 and cos 0=1.
= $\dfrac{1} {s^2 +1}$
So the Laplace transform of sint is equal to 1/(s2+1) and this is proved by the definition of Laplace transforms. That is,
| L{sint} = 1/(s2+1). |
Related Topics:
Laplace transform of unit step function
Laplace transform of Dirac delta function
FAQs
Q1: What is the Laplace transform of sint?
Answer: The Laplace transform of sint is equal to 1/(s2+1).
Q2: Find L{sin t}.
Answer: L{sin t} = 1/(s2+1).