The derivative of e^cosx (e to the power cosx) is equal to -sinx ecosx. In this post, we will find the derivative of ecosx by first principle.
The derivative formula of ecosx is given below:
$\dfrac{d}{dx}$(ecosx) = -sinx ecosx.
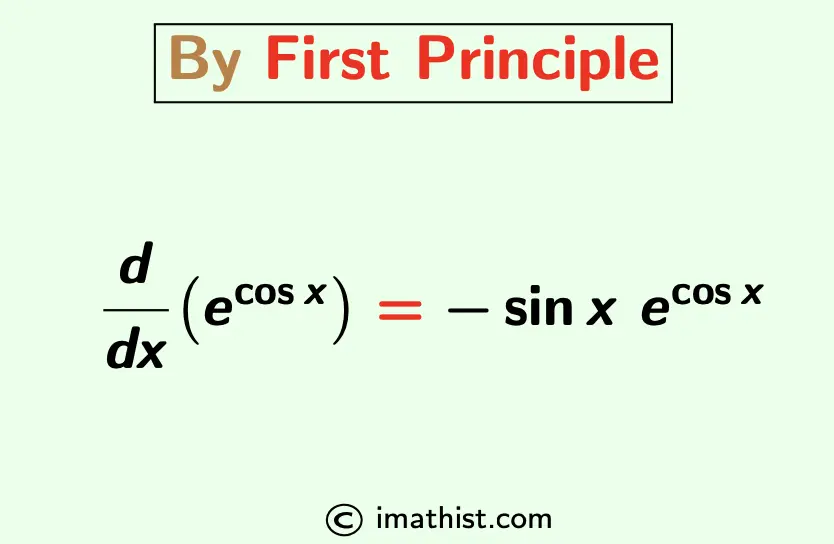
Derivative of e^cosx Using First Principle
By first principle, the derivative of a function f(x) using the first principle is given by the following limit formula:
$\dfrac{d}{dx}$ ( f(x) ) = limh→0 $\dfrac{f(x+h)-f(x)}{h}$.
Put f(x) = ecosx.
So $\dfrac{d}{dx}$ ( ecosx ) = limh→0 $\dfrac{e^{\cos(x+h)} – e^{\cos x}}{h}$
= limh→0 $\dfrac{e^{\cos x}(e^{\cos(x+h)-\cos x} -1)}{h}$
= ecosx limh→0 $\dfrac{e^{\cos(x+h)-\cos x} -1}{h}$
= ecosx limh→0 $\dfrac{e^{\cos(x+h)-\cos x} -1}{\cos(x+h)-\cos x}$ × limh→0 $\dfrac{\cos(x+h)-\cos x}{h}$
[Let z=cos(x+h) -cosx. Then z→0 as h→0]
= ecosx limz→0 $\dfrac{e^z-1}{z}$ × limh→0 $\dfrac{-2\sin(x+\frac{h}{2})\sin \frac{h}{2}}{h}$, using the formula cosa – cosb= – 2 sin(a+b)/2 sin(a-b)/2.
= ecosx × 1 × limh→0 $- \sin(x+\frac{h}{2})$ × limh→0 $\dfrac{\sin \frac{h}{2}}{\frac{h}{2}}$ using the limit formula limt→0(et-1)/t =1.
= – ecosx $\sin(x+\frac{0}{2})$ × limu→0 sinu/u where u=h/2.
= – sinx ecosx as the limit of sinx/x is 1 when x→0.
So the derivative of e^cosx is equal to -sinx ecosx, and this is obtained by the first principle of derivatives.
More Derivatives: Derivative of esinx by first principle
FAQs
Q1: What is the derivative of e^cosx?
Answer: The derivative of e^cosx is equal to -sinx ecosx.