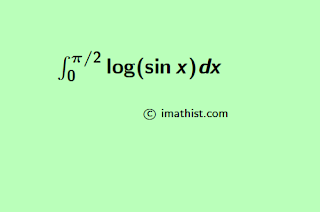
The integration of log(sin x) from 0 to pi/2 is -π/2 log2. In this section, we will find the integral of log sinx from 0 to pi/2. The following property will be used to calculate the integral.
$\int_0^af(x)dx=\int_0^af(a-x)dx$ …(i)
Integral of log(sin x) from 0 to pi/2
Question:
Show that $\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \log \sin x dx = – \frac{\pi}{2} \log 2$
Solution:
Let I = $\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}$ log sinx dx …(ii)
Using the above property (i), we have
I = $\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}$ log sinx dx = $\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}$ log sin($\frac{\pi}{2}$-x)dx.
By the fact $\sin(\frac{\pi}{2}-x)=\cos x$ we get that
$I=\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}\log \cos x dx$ ...(iii)
Adding (ii) and (iii), we obtain that
2I = $\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}$ (log sin x+log cos x)dx
⇒ 2I = $\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}$ log(sin x cos x)dx as log(a) + log(b)=log(ab)
⇒ 2I = $\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \log(\frac{\sin 2x}{2})dx$ as sin(2x)=2sin x cos x
⇒ 2I = $\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}(\log \sin 2x-\log 2)dx$ as log(a) – log(b)=log(a/b)
⇒ 2I = $\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}\log \sin 2x dx$ $- \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \log 2dx$
⇒ 2I = $\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}\log \sin 2x dx-\frac{\pi}{2}\log 2$ …(iv)
Let $I_1=\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}\log \sin 2xdx$
Put t=2x.
Therefore, dt=2 dx. Thus dx=dt/2.
Note that t=π when x=π/2 and t=0 when x=0.
So $I_1=\frac{1}{2}\int_0^\pi\log(\sin t) dt$ …(v)
Property: $\int_0^{2a}f(x)dx=2\int_0^a f(a-x)dx$ when $f(2a-x)=f(x)$
Observe that we have log(sin t)=log sin(π-t).
Thus, by the above property
$I_1=\frac{1}{2} \cdot 2 \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \log(\sin t) dt$
$=\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \log(\sin t) dt=I$
As $I_1=I$ we deduce from (iv) and (v) that
$2I =I-(\frac{\pi}{2})\log 2$
$\Rightarrow I=-\frac{\pi}{2} \log 2$
So we finally get that
$\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \log \sin x=-\frac{\pi}{2}\log 2$
Also Read:
Derivative of root(x)+1/root(x)
Q1: What is the integral of log sinx from 0 to pi/2?
Answer: The integration of log sinx from 0 to pi/2 is equal to -π/2 log2.